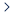Raspagem de dados da web de IA plano de proxy exclusivo [Tráfego ilimitado, largura de banda de 100 G+]


Residential Proxies adicionou 300,000 IP nos EUA a 9 de abril.


Raspagem de dados da web de IA plano de proxy exclusivo [Tráfego ilimitado, largura de banda de 100 G+]


Residential Proxies adicionou 300,000 IP nos EUA a 9 de abril.



Produtos
Beta
Serviços de proxy
Proxies Residenciais Dinâmicos
Rastreamento humanizado, sem proteção de IP. aproveite 200 milhões de IPs reais de mais de 195 locaisProxy de tráfego ilimitado AI
Uso ilimitado de proxies residenciais classificados, países atribuídos aleatoriamenteProxies do ISP
Equipe proxies residenciais estáticos (ISP) e desfrute de velocidade e estabilidade imbatíveisProxies estáticos de data center
Use IP de data center estável, rápido e poderoso em todo o mundoRotação de proxies de ISP
Extraia os dados necessários sem medo de ser bloqueadoProxies HTTP
Suporta protocolo completo http/https/socks5, alta segurança, alta estabilidade, alta conectividadeProxies Meias5
Forneça o melhor serviço de proxy para minimizar o custo de IP
Preço
$0.77/GB
Proxies residenciais
Proxies do ISP
Use settings
OBTER API
ferramentas
Ferramentas auxiliares
recurso
Recurso
início rápido
GUIA DO USUÁRIO
Exclusivo Empresarial
Revendedor

$0
Identidade não verificada

Visão geral

Fuso horário local

Utilizar o fuso horário local do dispositivo
(UTC+0:00) Horário de Greenwich
(UTC-8:00) Horário do Pacífico (EUA e Canadá)
(UTC-7:00) Arizona (EUA)
(UTC+8:00) Hong Kong (CN), Singapura

Conta

Autenticação de identidade
Sair