आवासीय प्रॉक्सीज़ ने 23 अप्रैल को 220,000 यूएस आईपी जोड़े।


AI वेब डेटा स्क्रैपिंग अनन्य प्रॉक्सी योजना [ असीमित ट्रैफ़िक, 100G+ बैंडविड्थ ]


आवासीय प्रॉक्सीज़ ने 23 अप्रैल को 220,000 यूएस आईपी जोड़े।


AI वेब डेटा स्क्रैपिंग अनन्य प्रॉक्सी योजना [ असीमित ट्रैफ़िक, 100G+ बैंडविड्थ ]

 Language
Language
Proxies
Earn Money
Referrals Program
Reseller Program
Local Time Zone
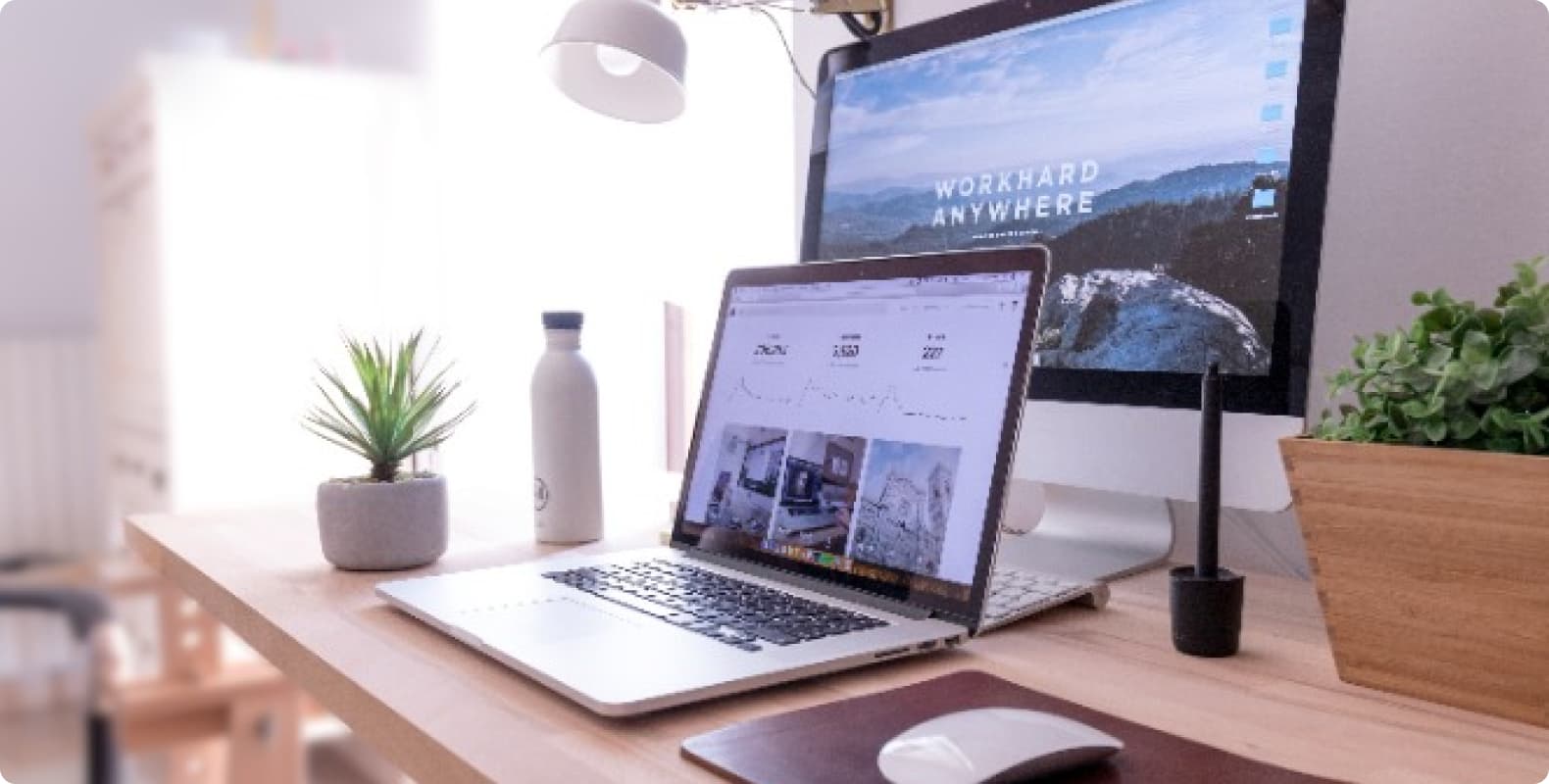




What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 in proxy configuration
In network communication, the IP address is an important element for identification and positioning. IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) are currently the most commonly used IP address protocol versions. In proxy configuration, understanding the difference between IPv4 and IPv6 is critical to ensuring network security and performance. This article will introduce the difference between IPv4 and IPv6
The difference between IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 is the earliest version of the IP address protocol, which consists of 32-bit binary numbers, usually expressed as four decimal numbers separated by dots (for example, 192.168.0.1). The IPv4 address space is limited and can only provide about 4.2 billion addresses, which leads to the shortage of IPv4 addresses. To solve this problem, IPv6 was introduced.
IPv6 is an upgraded version of IPv4, which consists of 128 binary digits, usually expressed as eight groups of hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (for example, 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334). The IPv6 address space is extremely large, and theoretically it can provide 34 billion trillion trillion addresses, which can almost meet the connection needs of an unlimited number of devices.
In addition to the difference in address space, IPv4 and IPv6 also have some differences in protocol functions. IPv6 supports better security and auto-configuration features, while also providing higher packet processing efficiency and flexibility. IPv6 also supports the IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) protocol, which is a security protocol at the network layer and can provide functions such as data encryption and identity verification.




For your payment security, please verify