When discussing Internet proxies, the two most commonly used types are residential proxies and datacenter proxies. Both act as an intermediary between users and the Internet, hiding the original IP address and providing an additional layer of anonymity. However, they differ greatly in terms of origin, usage, reliability, and anonymity. Choosing the right type of proxy depends on your needs, and understanding the key differences is essential to making the best decision.
In this blog, we will take an in-depth look at the differences between residential and datacenter proxies, including their features, benefits, limitations, and specific scenarios where each is best suited.
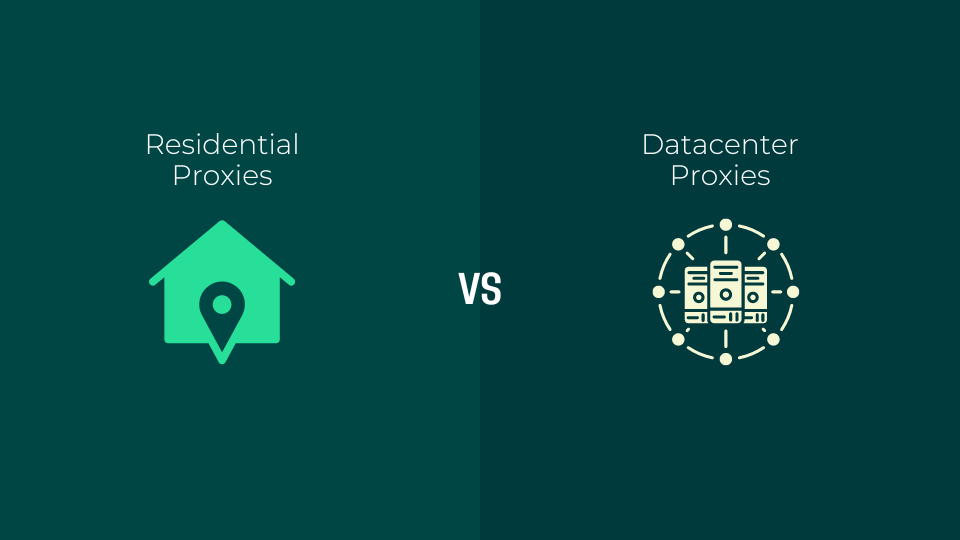
What is a residential proxy?
A residential proxy is an IP address that is provided by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) and assigned to a homeowner or individual. These IP addresses are associated with actual physical devices like smartphones, tablets, or computers, making them appear like real users when interacting with websites.
Key Features:
Legitimacy: Residential proxies come from real ISPs, which makes them appear like legitimate home users.
Device-Associated: They are tied to a physical address, which means it is harder for websites to detect and block them.
Reliability: Since residential IPs come from real users, they are generally more reliable for tasks that require high trust and a lower risk of being blocked.
Residential proxies are well suited for use cases that require high anonymity and acceptance, which may actively block non-residential traffic.
What are Data Center Proxies?
Data Center Proxies are IP addresses that are not associated with any ISP, but come from second-tier companies that provide a large number of IP addresses through data centers. These proxies are virtual and not directly connected to residential ISPs, which means they are often more easily identified as proxies by sophisticated websites.
Key Features:
No ISP Affiliation: Data center proxies are not provided by ISPs, which means they are less likely to be perceived as legitimate by certain websites.
Highly Scalable: These proxies are created in batches by cloud providers, making them easy to deploy and use at scale.
Faster but Riskier: While data center proxies are often very fast because they have the resources provided by powerful data centers, they are also more easily blocked because they lack the legitimacy of residential IPs.
Data center proxies are often used for general browsing, web scraping, or any scenario where speed is more important than a high level of anonymity.
Key Differences Between Residential and Data Center Proxies
1. Origin and Nature
Residential Proxies
Residential proxies are derived from IP addresses assigned to real residential locations by legitimate ISPs.
They represent actual home users and are associated with a specific geographic location.
Data Center Proxies
Data Center proxies originate from data centers and are not linked to ISPs or residential addresses.
These proxies are provided by third-party servers and lack the appearance of real residential users.
2. Anonymity and Detection
Residential Proxies
Residential proxies offer a higher level of anonymity because they are associated with real users and physical locations.
It is often difficult for websites to distinguish these IPs from real visitors, making them ideal for sensitive operations such as accessing restricted content or purchasing limited edition products.
Data Center Proxies
Data Center proxies are more easily blocked by websites that use advanced anti-proxy detection measures.
Since they do not belong to actual residential users, many websites can identify and block data center IPs, especially when they are from the same subnet.
3. Cost
Residential Proxies
Residential proxies are generally more expensive because they provide high-quality anonymity and legitimacy.
The infrastructure behind residential proxies is complex and usually requires the use of large P2P networks involving real equipment, which increases costs.
Data Center Proxies
Data center proxies are less expensive because they are generated in batches by data centers.
Their affordability makes them suitable for operations that require a large number of IPs, such as large-scale web scraping campaigns or testing website performance.
4. Speed and Performance
Residential Proxies
Residential proxies can be slower than data center proxies because they route traffic through the real ISP network.
Speeds may vary depending on the quality of your residential network and the number of users accessing at the same time.
Data Center Proxies
Data center proxies generally provide faster connections because they are hosted in powerful servers with high bandwidth.
They are particularly useful for tasks that require fast access and data throughput, such as crawling large amounts of data in a limited time.
Advantages of Residential Proxies
1. Real IP Appearance
Residential proxies come from real devices, which means they have a high degree of authenticity. This real appearance makes it difficult for websites to detect and block them, even with sophisticated anti-bot measures.
2. Access to restricted content
Many websites impose restrictions based on location or IP type. Residential proxies are particularly useful for accessing geo-blocked content, such as streaming services or local online marketplaces that restrict foreign users.
3. High success rate
For tasks such as web scraping, residential proxies have a much higher success rate than data center proxies. They are less likely to be flagged or blocked by websites, making them ideal for collecting data or conducting competitive analysis.
4. Better for sensitive activities
Residential proxies are often the first choice when dealing with sensitive activities such as sneaker rushes, ticket purchases, or social media management, as they minimize the risk of account suspensions or IP bans.
Advantages of Data Center Proxies
1. Economical and efficient
Data center proxies are much cheaper than residential proxies, making them more accessible to users who need to use multiple IPs at a low cost. This affordability is particularly beneficial for tasks that require a large number of concurrent connections.
2. High Speed
Data center proxies offer high-speed Internet connections, making them ideal for tasks that require a lot of bandwidth, such as testing websites, playing online games, or performing large-scale data collection.
3. Scalability
Data center proxies can be generated in large numbers, which means they are highly scalable. This feature makes them ideal for organizations that need thousands of IP addresses for large-scale operations, such as ad verification or automated testing.
4. Suitable for non-sensitive tasks
For tasks that do not require the highest anonymity, such as accessing public information, testing website performance, or scraping data from less stringent websites, data center proxies are often sufficient.
Conclusion
Choosing between residential and datacenter proxies depends largely on your specific needs and priorities. If you require high anonymity, real IP addresses, and the ability to bypass strict anti-bot measures, then residential proxies are your best choice. On the other hand, if you are concerned about cost-effectiveness, speed, and scalability, and these tasks do not require a high level of anonymity, then datacenter proxies will provide a practical solution. We hope that the information provided is helpful to you. However, if you still have any questions, please feel free to contact us at [email protected] or online chat.